Experimental and computational evidence for alpha-lactone intermediates in the addition of aqueous bromine to disodium dimethyl-maleate and -fumarate.
Necmettin Pirinççioğlu, James J Robinson, Mary F Mahon, J Grant Buchanan, Ian H Williams
文献索引:Org. Biomol. Chem. 5(24) , 4001-9, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Structural analysis of the bromo-beta-lactones obtained by addition of bromine to aqueous solutions of disodium 2,3-dimethylmaleate and 2,3-dimethylfumarate reveals stereochemistries opposite to those originally assigned in 1937: cis alkene yields erythro lactone, and trans alkene yields threo lactone. B3LYP/6-31+G(d) calculations using a PCM description of aqueous solvation confirm the validity of our proposed mechanism, in which the first-formed intermediate in each case is an alpha-lactone. The cyclic bromonium species is not an intermediate. An alternative pathway leading directly from cis alkene to cis lactone, via an unusual frontside displacement mechanism, is over 20 kJ mol(-1) higher in free energy. Hydrolysis of the bromo-beta-lactones yields bromohydrins whose stereochemistries as determined by X-ray crystallography indicate stereospecific formation by acyl-oxygen cleavage of the lactone ring, again contrary to the original view.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
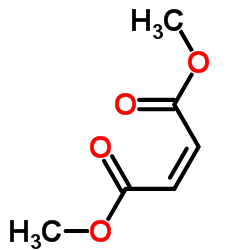 |
顺丁烯二甲酸二甲酯
CAS:624-48-6 |
C6H8O4 |
|
Fumarate analogs act as allosteric inhibitors of the human m...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9(6) , e98385, (2014)] |
|
Sensitization to dimethyl fumarate with multiple concurrent ...
2010-02-01 [Contact Dermatitis 62(2) , 88-96, (2010)] |
|
Use of p-nitrophenyl disulfide to measure reductive capacity...
1995-01-01 [Meth. Enzymol. 251 , 279-86, (1995)] |
|
Maleic acid dimethylester: evaluation of dermal toxicity and...
1991-08-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 29(8) , 575-8, (1991)] |
|
Facile synthesis of oxabicyclic alkenes by ultrasonication-p...
2004-08-20 [J. Org. Chem. 69(17) , 5763-5, (2004)] |