Neurotensin stimulates Cl(-) secretion in human colonic mucosa In vitro: role of adenosine.
M Riegler, I Castagliuolo, C Wang, M Wlk, T Sogukoglu, E Wenzl, J B Matthews, C Pothoulakis
文献索引:Gastroenterology 119(2) , 348-57, (2000)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Previous studies indicated that the peptide neurotensin (NT) stimulates Cl(-) secretion in animal small intestinal mucosa in vitro. In this study, we investigated whether NT causes Cl(-) secretion in human colonic mucosa and examined the mechanism of this response.Human mucosal preparations mounted in Ussing chambers were exposed to NT. Drugs for pharmacologic characterization of NT-induced responses were applied 30 minutes before NT.Serosal, but not luminal, administration of NT (10(-8) to 10(-6) mol/L) induced a rapid, monophasic, concentration- and chloride-dependent, bumetanide-sensitive short-circuit current (Isc) increase that was inhibited by the specific nonpeptide NT receptor antagonists SR 48692 and SR 142948A, the neuronal blocker tetrodotoxin, and the prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor indomethacin. The mast cell stabilizer lodoxamide and the histamine 1 and 2 receptor antagonists pyrilamine and ranitidine, respectively, did not significantly alter NT-induced Isc increase. In contrast, the adenosine receptor 1 and 2 antagonists inhibited this secretory response, whereas the adenosine uptake inhibitors S-(4-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioguanosine and S-(4-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioinosine and the adenosine deaminase inhibitor deoxycoformycin potentiated NT-induced Isc increase. Serosal adenosine induced a rapid, monophasic, concentration- and chloride-dependent, bumetanide-sensitive Isc increase.NT stimulates chloride secretion in human colon by a pathway(s) involving mucosal nerves, adenosine, and prostaglandins.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
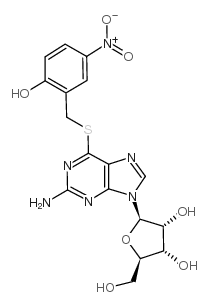 |
S-(2-羟基-5-硝基苄基)-6-硫鸟嘌呤
CAS:41094-07-9 |
C17H18N6O7S |
|
Inhibitors of nucleoside transport. A structure-activity stu...
1975-10-01 [J. Med. Chem. 18 , 968, (1975)] |
|
Mechanism of urate production by guinea-pig ileum.
1986-01-01 [Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 195 Pt B , 239-43, (1986)] |
|
Potentiation of methotrexate lymphocytotoxicity in vitro by ...
1989-03-01 [Br. J. Cancer 59(3) , 381-4, (1989)] |
|
The effect of pH on interaction of nitrobenzylthioinosine an...
1985-07-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 27(6) , 662-5, (1985)] |
|
Adenosine and ATP effects on isolated guinea pig gallbladder...
1983-09-01 [Pflugers Arch. 399(1) , 42-5, (1983)] |