COX-2 suppresses tissue factor expression via endocannabinoid-directed PPARdelta activation.
Mallika Ghosh, Haibin Wang, Youxi Ai, Elisa Romeo, James P Luyendyk, Jeffrey M Peters, Nigel Mackman, Sudhansu K Dey, Timothy Hla
文献索引:J. Exp. Med. 204 , 2053-61, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Although cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitors (coxibs) are effective in controlling inflammation, pain, and tumorigenesis, their use is limited by the recent revelation of increased adverse cardiovascular events. The mechanistic basis of this side effect is not well understood. We show that the metabolism of endocannabinoids by the endothelial cell COX-2 coupled to the prostacyclin (PGI(2)) synthase (PGIS) activates the nuclear receptor peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) delta, which negatively regulates the expression of tissue factor (TF), the primary initiator of blood coagulation. Coxibs suppress PPARdelta activity and induce TF expression in vascular endothelium and elevate circulating TF activity in vivo. Importantly, PPARdelta agonists suppress coxib-induced TF expression and decrease circulating TF activity. We provide evidence that COX-2-dependent attenuation of TF expression is abrogated by coxibs, which may explain the prothrombotic side-effects for this class of drugs. Furthermore, PPARdelta agonists may be used therapeutically to suppress coxib-induced cardiovascular side effects.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
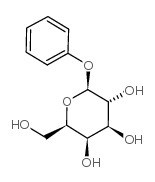 |
苯基β-D-吡喃半乳糖苷
CAS:2818-58-8 |
C12H16O6 |
|
Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects mouse brain against D-g...
2015-06-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 133 , 122-31, (2015)] |
|
Structure-based drug design and optimization of mannoside ba...
2010-06-24 [J. Med. Chem. 53 , 4779-92, (2010)] |
|
Transdifferentiation of mouse adipose-derived stromal cells ...
2015-05-15 [Exp. Cell Res. 334 , 160-72, (2015)] |
|
Drosophila KASH-domain protein Klarsicht regulates microtubu...
2015-11-01 [Dev. Biol. 407 , 103-14, (2015)] |
|
FimH antagonists for the oral treatment of urinary tract inf...
2010-12-23 [J. Med. Chem. 53 , 8627-41, (2010)] |