Midodrine hydrochloride and L-threo-3,4-dihydroxy-phenylserine preserve cerebral blood flow in hemodialysis patients with orthostatic hypotension.
Kiichiro Fujisaki, Hidetoshi Kanai, Hideki Hirakata, Sachiko Nakamura, Yuko Koga, Fumitada Hattori, Mitsuo Iida
文献索引:Ther. Apher. Dial. 11(1) , 49-55, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Orthostatic hypotension (OH) after hemodialysis (HD) is a serious complication, as it causes various neurological symptoms and even ischemic brain damage. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of antihypotensive agents, midodrine hydrochloride (MID) and L-threo-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine (L-DOPS), on OH after HD. We measured systolic blood pressure (SBP) and cerebral blood flow velocity in the middle cerebral artery (MCVm, by transcranial Doppler sonography), in patients with OH during a 5-min 60-degree head-up tilt test at both before and after 4-week treatment with MID at 4 mg/day (N = 6) or L-DOPS at 400 mg/day (N = 7). Both MID and L-DOPS did not significantly protect against falls in systolic BP (SBP) after passive head-up tilt. However, a significant improvement was achieved in MCVm-decrement in the MID group at 3 min and the L-DOPS group at 0, 1 and 3 min during head-up tilt. Although MID and L-DOPS did not prevent OH after HD in HD patients, both agents preserved cerebral blood flow during orthostasis in HD patients with OH.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
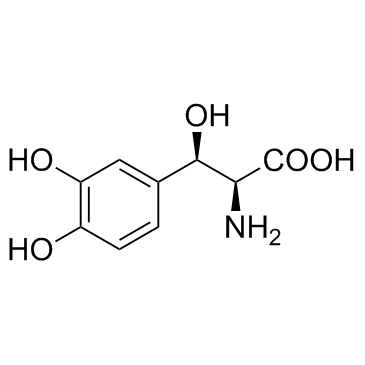 |
屈西多巴
CAS:23651-95-8 |
C9H11NO5 |
|
Application of the BCS biowaiver approach to assessing bioeq...
2014-11-20 [Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 64 , 37-43, (2014)] |
|
[Acute poisoning of droxidopa: report of a case].
2013-09-01 [Chudoku. Kenkyu. 26(3) , 244-5, (2013)] |
|
The noradrenaline precursor L-DOPS reduces pathology in a mo...
2012-01-01 [Neurobiol. Aging 33(8) , 1651-63, (2012)] |
|
Comment on "Midodrine hydrochloride and L-threo-3,4-dihydrox...
2007-10-01 [Ther. Apher. Dial. 11(5) , 407-8, (2007)] |
|
Randomized withdrawal study of patients with symptomatic neu...
2015-01-01 [Hypertension 65(1) , 101-7, (2015)] |