Ultrasonic degradation of schizophyllan, an antitumor polysaccharide produced by Schizophyllum commune Fries.
K Tabata, W Ito, T Kojima, S Kawabata, A Misaki
文献索引:Carbohydr. Res. 89 , 121, (1981)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Schizophyllan, a water-soluble beta-D-glucan elaborated by Schizophyllum commune Fries, was partially depolymerized by ultrasonic irradiation to a low-molecular-weight polysaccharide, designated "sonic-degraded schizophyllan". Both native and degraded polysaccharides exhibited essentially the same antitumor activities against Sarcoma-180 ascites. Both glucans are comprised solely of D-glucose residues and have a main chain of (1 leads to 3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl residues, one out of three glucose residues being attached as single, (1 leads to 6)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl groups. Although both glucans have similar structural features, significant differences are observed in such physical properties as molecular weight and intrinsic viscosity. End-group analysis by using radioisotope-labeled glucans suggests that ultrasonic degradation occurs mainly by cleavage of glycosidic bonds of the main chain of schizophyllan. The molecular weights of the native and sonic-degraded schizophyllan were shown to be 75% of those of corresponding, original schizophyllan preparations, suggesting that there is no anomalous linkage sensitive to periodate oxidation, and ultrasonic irradiation may cause random hydrolysis of (1 leads to 3)-beta-D-glucosidic linkages in the main chain.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
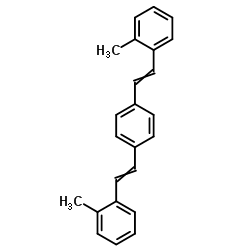 |
1,4-双(2-甲基苯乙烯基)苯
CAS:13280-61-0 |
C24H22 |
|
Radionuclide sensors based on chemically selective scintilla...
1999-12-01 [Anal. Chem. 71 , 5420, (1999)] |
|
Evaluation of flow cell detector configurations combining si...
2006-04-01 [Anal. Chem. 78 , 2254, (2006)] |
|
Determination of 235U/238U atom ratio in uranium samples usi...
2009-01-15 [Analyst 119 , 465, (1994)] |
|
Fluorescence anisotropy of tyrosinate anion using one-, two-...
2013-03-01 [J. Fluoresc. 23 , 339-47, (2013)] |
|
Two-photon absorption cross-sections of reference dyes: a cr...
2008-01-11 [ChemPhysChem 9(1) , 111-6, (2008)] |