| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
磷胺
CAS:13171-21-6 |
|
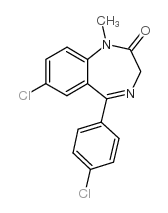 |
4'-氯地西泮
CAS:14439-61-3 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
磷胺
CAS:13171-21-6 |
|
 |
4'-氯地西泮
CAS:14439-61-3 |