Extended Hildebrand solubility approach: solubility of tolbutamide, acetohexamide, and sulfisomidine in binary solvent mixtures.
A Martin, M J Miralles
文献索引:J. Pharm. Sci. 71(4) , 439-42, (1982)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The extended Hildebrand approach for predicting solubilities of crystalline compounds in solvent mixtures was tested using tolbutamide, acetohexamide, and sulfisomidine in mixed solvents consisting of hexane-absolute ethanol and 95% (v/v) ethyl alcohol-aqueous buffer. The solubility of these drugs was determined at 25 +/- 0.2 degrees and then back-calculated using the adhesive energy term, W, to account for solute-solvent interaction. Solubilities were predicted within 13% for tolbutamide, 31% for acetohexamide, and 43% for sulfisomidine, and with considerably better accuracy in most solvent mixtures.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
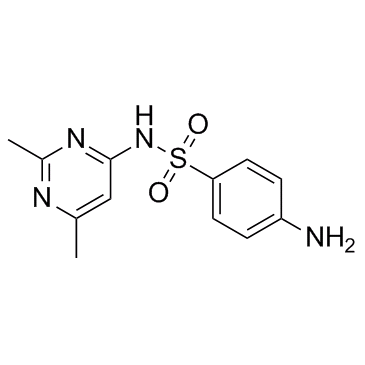 |
磺胺索嘧啶
CAS:515-64-0 |
C12H14N4O2S |
|
Fast determination of 22 sulfonamides from chicken breast mu...
2014-06-06 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1345 , 17-28, (2014)] |
|
Multiresidue analysis of sulfonamides, quinolones, and tetra...
2016-08-01 [Food Chem. 204 , 252-62, (2016)] |
|
Coulometric determination of sulphisomidine, sulphamethoxydi...
1991-01-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 9(2) , 199-201, (1991)] |
|
Identification of the 'wrong' active pharmaceutical ingredie...
2003-01-01 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 17(3) , 215-21, (2003)] |
|
Lack of oxidative pathways in the metabolism of sulphisomidi...
1989-12-01 [J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 12(4) , 459-62, (1989)] |