Identification of the 'wrong' active pharmaceutical ingredient in a counterfeit Halfan drug product using accurate mass electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry, accurate mass tandem mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.
Jean-Claude Wolff, Linda A Thomson, Christine Eckers
文献索引:Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 17(3) , 215-21, (2003)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Methodology is presented for identifying an unknown active (pharmaceutical) ingredient (AI) in a counterfeit drug product. A range of mass spectrometric techniques, i.e., accurate mass mass spectrometry, tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS), has been employed to determine the AI in a counterfeit Halfan suspension, an antimalarial drug. In particular, use of LockSpray accurate mass MS/MS allowed identification of parts of the molecule from fragments, hence limiting the number of possible elemental compositions for the nominal mass of 278 found for the AI in the counterfeit product. The analysis of the isotope pattern observed for the protonated molecule further reduced the number of possible elemental compositions. A literature search for readily commercially available compounds of molecular formula C(12)H(14)N(4)O(2)S suggested that the AI was either sulfamethazine or sulfisomidine. An LC/MS separation of those two compounds and reference MS/MS spectra obtained for sulfamethazine and sulfisomidine led to the conclusion that the AI in the counterfeit Halfan suspension is sulfamethazine, which is an antibacterial agent.Copyright 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
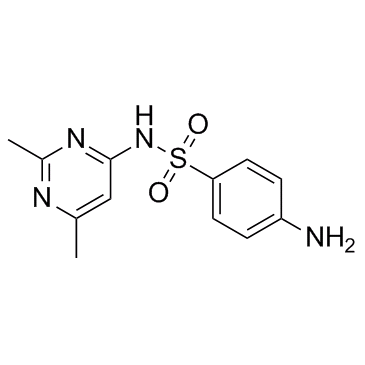 |
磺胺索嘧啶
CAS:515-64-0 |
C12H14N4O2S |
|
Fast determination of 22 sulfonamides from chicken breast mu...
2014-06-06 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1345 , 17-28, (2014)] |
|
Multiresidue analysis of sulfonamides, quinolones, and tetra...
2016-08-01 [Food Chem. 204 , 252-62, (2016)] |
|
Coulometric determination of sulphisomidine, sulphamethoxydi...
1991-01-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 9(2) , 199-201, (1991)] |
|
Lack of oxidative pathways in the metabolism of sulphisomidi...
1989-12-01 [J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 12(4) , 459-62, (1989)] |
|
Extended Hildebrand solubility approach: solubility of tolbu...
1982-04-01 [J. Pharm. Sci. 71(4) , 439-42, (1982)] |