Preferential block of desensitizing AMPA receptor in hippocampal neurons by gamma-D-glutamylaminomethylsulfonic acid.
V W Wilsch, V I Pidoplichko, K G Reymann
文献索引:Eur. J. Pharmacol. 284 , 141-147, (1995)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The (RS)-alpha-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolopropionic acid (AMPA)/kainate receptor-channel complex mediates fast components of excitatory synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Distinguishing between these components is a difficult pharmacological task. As was recently reported, gamma-D-glutamylaminomethylsulfonic acid (GAMS) may be a selective kainate receptor antagonist. We have tested this possibility in experiments which were carried out on acutely isolated rat hippocampal neurons. It appeared that 1 mM GAMS first blocked 83 +/- 1% of the fast desensitizing 128 microM AMPA-gated current, but only 38 +/- 6% of the non-desensitizing current component and reached, at higher GAMS concentrations, a plateau at about 50% of the control steady state current level. In contrast to the blocking action of GAMS on AMPA-gated currents, 4-fold higher concentrations of GAMS were needed to block currents elicited by 256 microM kainate application. It is suggested that several subunit compositions of the AMPA-gated receptor could coexist on a single hippocampal cell. Furthermore, GAMS has a certain preference for subunit assemblies which could mediate fast desensitizing and, a portion of, the non-desensitizing current component.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
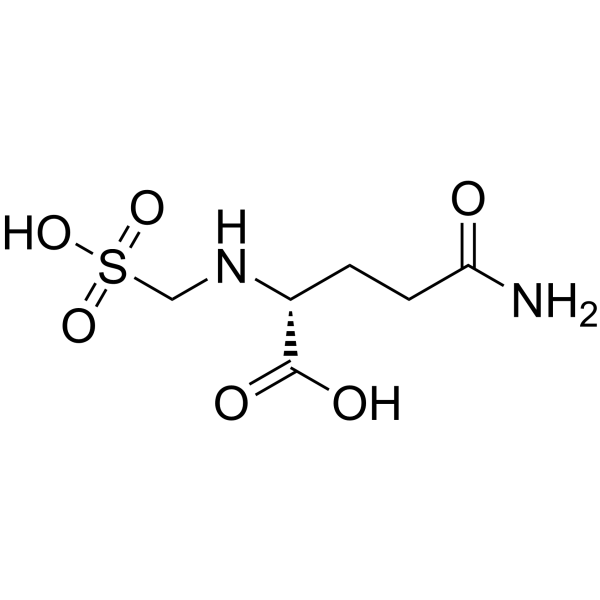 |
γ-D-谷氨酰胺基甲基磺酸
CAS:90237-02-8 |
C6H12N2O6S |
|
Effects of some excitatory amino acid antagonists on imipene...
1995-02-06 [Brain Res. 671(1) , 131-40, (1995)] |
|
Glutamate and vasopressin interact to control scent marking ...
1996-08-26 [Brain Res. 731(1-2) , 213-6, (1996)] |
|
Excitatory neurotransmitters in the lateral habenula and ped...
1992-09-25 [Brain Res. 591(2) , 209-22, (1992)] |
|
Evidence for an involvement of NMDA and non-NMDA receptors i...
1991-09-16 [Neurosci. Lett. 130(2) , 271-4, (1991)] |
|
Release of GABA from sensory neurons transduced with a GAD67...
2006-02-16 [Brain Res. 1073-1074 , 297-304, (2006)] |