Release of GABA from sensory neurons transduced with a GAD67-expressing vector occurs by non-vesicular mechanisms.
Jun Liu, Changfeng Tai, William C de Groat, Xiang-min Peng, Marina Mata, David J Fink
文献索引:Brain Res. 1073-1074 , 297-304, (2006)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We have demonstrated that dorsal root ganglion neurons transduced with a recombinant replication-defective herpes simplex virus vector coding for glutamic acid decarboxylase (QHGAD67) release GABA to produce an analgesic effect in rodent models of pain. In this study, we examined the mechanism of transgene-mediated GABA release from dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro and in vivo. Release of GABA from dorsal root ganglion neurons transduced with QHGAD67 was not increased by membrane depolarization induced by 60 mM extracellular K+ nor reduced by the removal of Ca2+ from the medium. Release of GABA from transduced dorsal root ganglion neurons was, however, blocked in a dose-dependent manner by NO-711, a selective inhibitor of the GABA transporter-1. The amount of GABA released from a spinal cord slice preparation, prepared from animals transduced by subcutaneous inoculation of QHGAD67 in the hind paws, was substantially increased compared to animals transduced with control vector Q0ZHG or normal animals, but the amount of GABA released was not changed by stimulation of the dorsal roots at either low (0.1 mA, 0.5-ms duration) or high (10 mA, 0.5-ms duration) intensity. We conclude that QHGAD67-mediated GABA release from dorsal root ganglion neurons is non-vesicular, independent of electrical depolarization, and that this efflux is mediated through reversal of the GABA transporter.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
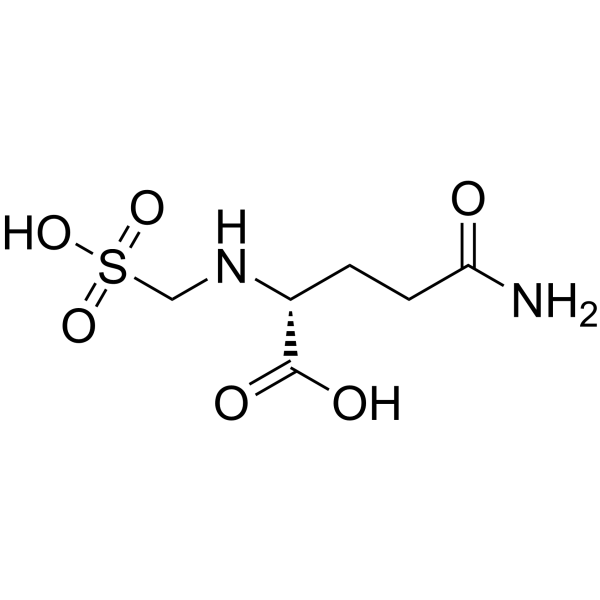 |
γ-D-谷氨酰胺基甲基磺酸
CAS:90237-02-8 |
C6H12N2O6S |
|
Effects of some excitatory amino acid antagonists on imipene...
1995-02-06 [Brain Res. 671(1) , 131-40, (1995)] |
|
Glutamate and vasopressin interact to control scent marking ...
1996-08-26 [Brain Res. 731(1-2) , 213-6, (1996)] |
|
Excitatory neurotransmitters in the lateral habenula and ped...
1992-09-25 [Brain Res. 591(2) , 209-22, (1992)] |
|
Evidence for an involvement of NMDA and non-NMDA receptors i...
1991-09-16 [Neurosci. Lett. 130(2) , 271-4, (1991)] |
|
Preferential block of desensitizing AMPA receptor in hippoca...
1995-09-15 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 284 , 141-147, (1995)] |