Similar renoprotection after renin-angiotensin-dependent and -independent antihypertensive therapy in 5/6-nephrectomized Ren-2 transgenic rats: are there blood pressure-independent effects?
Petr Kujal, Věra Čertíková Chábová, Zdenka Vernerová, Agnieszka Walkowska, Elzbieta Kompanowska-Jezierska, Janusz Sadowski, Zdeňka Vaňourková, Zuzana Husková, Martin Opočenský, Petra Skaroupková, Stanislava Schejbalová, Herbert J Kramer, Dan Rakušan, Jan Malý, Ivan Netuka, Ivana Vaněčková, Libor Kopkan, Luděk Cervenka
文献索引:Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 37(12) , 1159-69, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
1. Hypertension plays a critical role in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), but it has also been postulated that antihypertensive drugs that block the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) show class-specific renoprotective actions beyond their blood pressure (BP)-lowering effects. 2. Because this notion has recently been questioned, in the present study we compared the effects of a RAS-dependent antihypertensive therapy (a combination of trandolapril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) and losartan, an angiotensin-II (AngII) receptor subtype 1A receptor antagonist) with a 'RAS-independent' antihypertensive therapy (a combination of labetalol, an alfa- and beta-adrenoreceptor antagonist with the diuretics, hydrochlorothiazide and furosemide) on the progression of CKD after 5/6 renal ablation (5/6 NX) in Ren-2 renin transgenic rats (TGR), a model of AngII-dependent hypertension. Normotensive transgene-negative Hannover Sprague-Dawley (HanSD) rats after 5/6 NX served as controls. 3. RAS-dependent and -independent antihypertensive therapies normalized BP and survival rate, and prevented the development of cardiac hypertrophy and glomerulosclerosis to the same degree in 5/6 NX HanSD rats and in 5/6 NX TGR. The present findings show that renoprotection, at least in rats after 5/6 NX, is predominantly BP-dependent. When equal lowering of BP was achieved, leading to normotension, cardio- and renoprotective effects were equivalent irrespective of the type of antihypertensive therapy. 4. These findings should be taken into consideration in attempts to develop new therapeutic approaches and strategies aimed to prevent the progression of CKD and to lower the incidence of ESRD.© 2010 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology © 2010 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
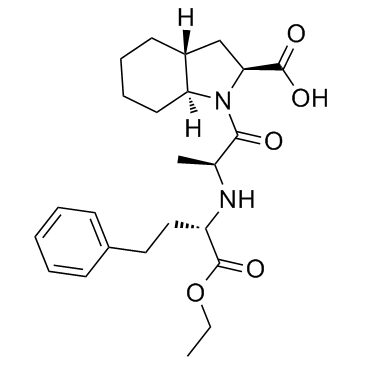 |
群多普利
CAS:87679-37-6 |
C24H34N2O5 |
|
Tarka® (trandolapril/verapamil hydrochloride extended-releas...
2011-03-01 [J. Emerg. Med. 40(3) , 291-5, (2011)] |
|
Dual therapy versus monotherapy of trandolapril and telmisar...
2011-09-01 [J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 12(3) , 169-75, (2011)] |
|
Tarka® overdose in a young child.
2011-09-01 [Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 30(9) , 1392-8, (2011)] |
|
Trandolapril, but not verapamil nor their association, resto...
2011-06-01 [Transl. Res. 157(6) , 348-56, (2011)] |
|
Safety profile of the combination of verapamil and trandolap...
1997-03-01 [J. Hypertens. Suppl. 15(2) , S51-3, (1997)] |