Glibenclamide acts as an inhibitor of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase enzyme.
N Ohgami, A Kuniyasu, K Furukawa, A Miyazaki, H Hakamata, S Horiuchi, H Nakayama
文献索引:Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277(2) , 417-22, (2000)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Sulfonylureas are used in the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Little is known, however, about their effects on cholesterol metabolism. We tested in the present study the effects of glibenclamide (GB) on cholesterol esterification (CE) in macrophage-derived cells. GB inhibited intracellular accumulation of CE induced by acetylated LDL or oxidized LDL in J774 cells, but no such effect on total cholesterol, suggesting that the target of GB was acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT). In the cell-free reconstitution ACAT assay, GB inhibited the ACAT activity with an IC(50) value of 20 microM. Furthermore, GB effectively inhibited the ACAT activity of PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells to the undifferentiated level of THP-1. In the whole-cell ACAT assay using CHO cells overexpressed with ACAT-1 or ACAT-2, GB inhibited the activity of both isozymes with similar potency. Our in vitro data suggest that sulfonylurea could be a potential seed for a new generation of ACAT inhibitors.Copyright 2000 Academic Press.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
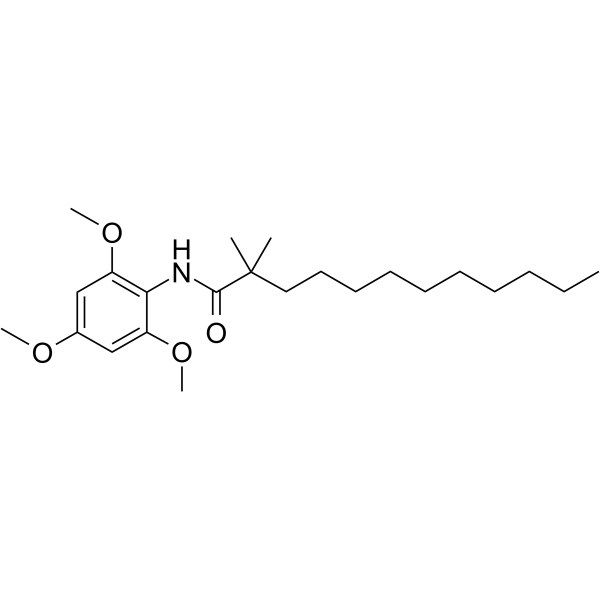 |
2,2-二甲基-N-(2,4,6-三甲氧基苯基)月桂酰胺
CAS:114289-47-3 |
C23H39NO4 |
|
cPLA2α and EHD1 interact and regulate the vesiculation of ch...
2012-05-01 [Mol. Biol. Cell 23(10) , 1874-88, (2012)] |
|
Use of acyltransferase inhibitors to block vesicular traffic...
2005-01-01 [Meth. Enzymol. 404 , 115-25, (2005)] |
|
A unique lysophospholipid acyltransferase (LPAT) antagonist,...
2005-07-15 [J. Cell Sci. 118(Pt 14) , 3061-71, (2005)] |
|
In vitro and in vivo disposition of 2,2-dimethyl-N-(2,4,6-tr...
1997-01-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 25(1) , 123-30, (1997)] |
|
The lysophospholipid acyltransferase antagonist CI-976 inhib...
2008-05-01 [Traffic 9(5) , 786-97, (2008)] |