The lysophospholipid acyltransferase antagonist CI-976 inhibits a late step in COPII vesicle budding.
William J Brown, Helen Plutner, Daniel Drecktrah, Bret L Judson, William E Balch
文献索引:Traffic 9(5) , 786-97, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The mechanism of coat protein (COP)II vesicle fission from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) remains unclear. Lysophospholipid acyltransferases (LPATs) catalyze the conversion of various lysophospholipids to phospholipids, a process that can promote spontaneous changes in membrane curvature. Here, we show that 2,2-methyl-N-(2,4,6,-trimethoxyphenyl)dodecanamide (CI-976), a potent LPAT inhibitor, reversibly inhibited export from the ER in vivo and the formation of COPII vesicles in vitro. Moreover, CI-976 caused the rapid and reversible accumulation of cargo at ER exit sites (ERESs) containing the COPII coat components Sec23/24 and Sec13/31 and a marked enhancement of Sar1p-mediated tubule formation from ERESs, suggesting that CI-976 inhibits the fission of assembled COPII budding elements. These results identify a small molecule inhibitor of a very late step in COPII vesicle formation, consistent with fission inhibition, and demonstrate that this step is likely facilitated by an ER-associated LPAT.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
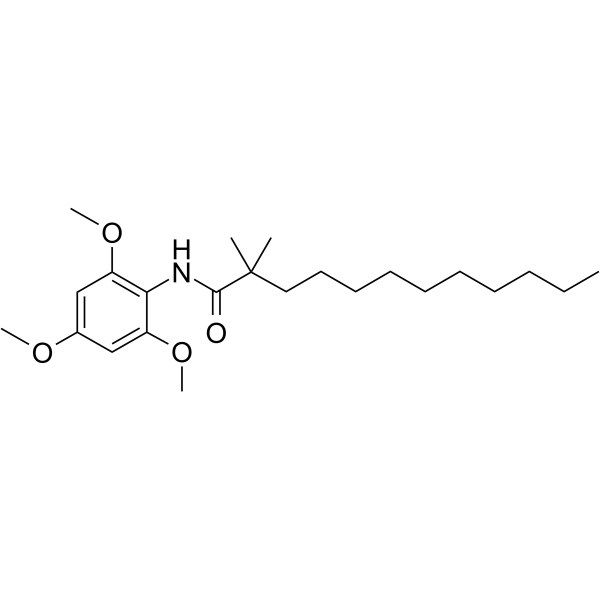 |
2,2-二甲基-N-(2,4,6-三甲氧基苯基)月桂酰胺
CAS:114289-47-3 |
C23H39NO4 |
|
cPLA2α and EHD1 interact and regulate the vesiculation of ch...
2012-05-01 [Mol. Biol. Cell 23(10) , 1874-88, (2012)] |
|
Use of acyltransferase inhibitors to block vesicular traffic...
2005-01-01 [Meth. Enzymol. 404 , 115-25, (2005)] |
|
A unique lysophospholipid acyltransferase (LPAT) antagonist,...
2005-07-15 [J. Cell Sci. 118(Pt 14) , 3061-71, (2005)] |
|
In vitro and in vivo disposition of 2,2-dimethyl-N-(2,4,6-tr...
1997-01-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 25(1) , 123-30, (1997)] |
|
Iron loaded ferritin secretion and inhibition by CI-976 inAe...
2009-01-01 [Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 152(4) , 352-63, (2009)] |