Novel microbial metabolites of the phoslactomycins family induce production of colony-stimulating factors by bone marrow stromal cells. I. Taxonomy, fermentation and biological properties.
T Kohama, R Enokita, T Okazaki, H Miyaoka, A Torikata, M Inukai, I Kaneko, T Kagasaki, Y Sakaida, A Satoh
文献索引:J. Antibiot. 46(10) , 1503-11, (1993)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Three metabolites were isolated from the culture broth of an actinomycete strain identified as Streptomyces platensis SANK 60191, that induce the production of colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) by stromal cell line KM-102 at ED50 concentrations from 40 to 200 ng/ml. The compounds induced quantities of granulocyte CSF (G-CSF) and granulocyte-macrophage CSF (GM-CSF) comparable to those induced by interleukin-1, a strong CSF inducer. These metabolites were called leustroducsins (A, B and C) and were later found to be structurally related to phoslactomycins. This is the first report of CSF inducing activity by members of the phoslactomycin class.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
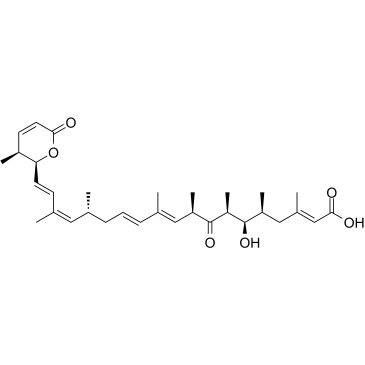 |
来普霉素A
CAS:87081-36-5 |
C32H46O6 |
|
Serine residue 115 of MAPK-activated protein kinase MK5 is c...
2011-03-01 [Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68 , 847-62, (2011)] |
|
Leptomycins A and B, new antifungal antibiotics. I. Taxonomy...
1983-06-01 [J. Antibiot. 36(6) , 639-45, (1983)] |
|
Leptomycins A and B, new antifungal antibiotics. II. Structu...
1983-06-01 [J. Antibiot. 36(6) , 646-50, (1983)] |
|
Phosphorylation and dimerization regulate nucleocytoplasmic ...
2002-04-05 [J. Biol. Chem. 277(14) , 12351-8, (2002)] |
|
[Leptomycin: a specific inhibitor of protein nuclear export]...
1999-07-01 [Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 44(9) , 1379-88, (1999)] |