| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
碱性磷酸酶
CAS:9001-78-9 |
|
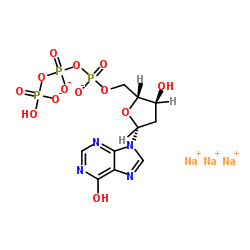 |
2’-脱氧肌苷三磷酸三钠盐
CAS:95648-77-4 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
碱性磷酸酶
CAS:9001-78-9 |
|
 |
2’-脱氧肌苷三磷酸三钠盐
CAS:95648-77-4 |