Early versus late hCG administration to trigger ovulation in mild stimulated IUI cycles: a randomized clinical trial.
Ana Luisa B da Silva, Elisangela Arbo, Renato Fanchin
文献索引:Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 164(2) , 156-60, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To verify non-inferiority of the clinical pregnancy rate of Early hCG administration (leading follicle sizes within 16.0-16.9 mm in diameter) compared to Late hCG administration (leading follicle sizes within 18.0-18.9 mm in diameter).Prospective randomized trial. Six hundred and twelve infertile women candidates for intrauterine insemination (IUI) received HP-hMG 75 IU/day SC from cycle days 4 to 8 and then as per ovarian response. Ovulation was randomly triggered (hCG 5000 IU, IM) when the leading follicle diameter ranged between either 16.0 and 16.9 mm (Early hCG group, n=227) or 18.0 and 18.9 mm (Late hCG group, n=207) and IUI was performed approximately 36 h later.Whereas population and sperm characteristics were comparable in both groups, the number of follicles ≥ 14 mm in diameter (P<0.007) and serum estradiol levels (P<0.001) on the day of hCG were lower in the Early versus the Late hCG groups. Clinical (11.9% versus 12.1%) and ongoing (11.0% versus 8.6%) pregnancy rates per randomized women were similar in the two groups and statistical non-inferiority of clinical and ongoing pregnancy rates was demonstrated.These results suggest that hCG administered when the largest follicle size reaches 16.0-16.9 mm leads to similar clinical and ongoing pregnancy rates as when it reaches 18.0-18.9 mm in IUI cycles.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
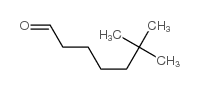 |
尿促性素
CAS:61489-71-2 |
C9H18O |
|
Gonadotropinoma presenting as a case of pseudo-ovarian failu...
2013-01-01 [Clin. Exp. Obstet. Gynecol. 40(2) , 295-6, (2013)] |
|
Re: Optimization of Spermatogenesis-Regulating Hormones in P...
2013-12-01 [J. Urol. 190(6) , 2209, (2013)] |
|
Clinical comparison of ovarian stimulation and luteal suppor...
2013-01-01 [J. Reprod. Med. 58(3-4) , 153-60, (2013)] |
|
LH supplementation in mild stimulations cycles without pitui...
2013-02-01 [Gynecol. Endocrinol. 29(2) , 101-4, (2013)] |
|
Modified repeated intracyclic clomiphene citrate therapy aft...
2012-01-01 [Clin. Exp. Obstet. Gynecol. 39(3) , 317-20, (2012)] |