Functional roles of NMDA receptor NR2A and NR2B subunits in the acute intoxicating effects of ethanol in mice.
Janel M Boyce-Rustay, Andrew Holmes
文献索引:Synapse 56(4) , 222-5, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The present study examined the roles of NR2A and NR2B subunit-containing NMDA receptors in the mediation of the sedative/hypnotic effects of ethanol in mice. The ability of the competitive NMDA antagonist, CGP-37849 (0, 1, or 3 mg/kg), and the NR2B-selective antagonist, Ro 25-6981 (0, 3, or 10 mg/kg), to alter (3 g/kg) ethanol-induced sleep time was measured in C57BL/6J mice and NR2A knockout (KO) mice. The results show that pretreatment with either antagonist significantly potentiated the sedative/hypnotic effects of ethanol in C57BL/6J mice. These effects were not significantly altered in NR2A KO mice. Basal sleep time responses to ethanol were also normal in NR2A KO mice. These findings confirm a major role for NMDA receptors in the acute intoxicating actions of ethanol and provide tentative support for a prepotent role of the NR2B subunit in these effects.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
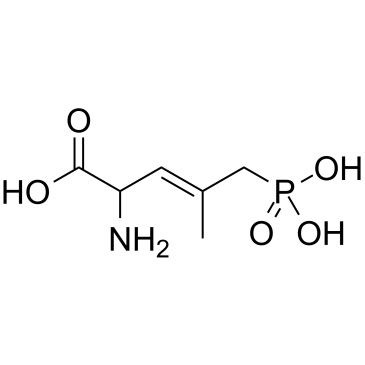 |
(E)-2-氨基-4-甲基-5-膦酰基-3-戊烯酸
CAS:127910-31-0 |
C6H12NO5P |
|
Involvement of voltage- and ligand-gated Ca2+ channels in th...
2003-05-01 [Kidney Int. 63(5) , 1764-75, (2003)] |
|
GSA: behavioral, histological, electrophysiological and neur...
2005-02-15 [Physiol. Behav. 84(2) , 251-64, (2005)] |
|
Competitive NMDA receptor antagonists and agonists: effects ...
2004-01-01 [Pol. J. Pharmacol. 56(1) , 59-66, (2004)] |
|
CGP 37849 and CGP 39551: novel competitive N-methyl-D-aspart...
1990-01-01 [Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 361 , 421-7, (1990)] |
|
NMDA/glutamate mechanism of magnesium-induced anxiolytic-lik...
2008-01-01 [Pharmacol. Rep. 60(5) , 655-63, (2008)] |