The effects of an essential fatty acid compound and a cholecystokinin-8 antagonist on iron deficiency induced anorexia and learning deficits.
Shlomo Yehuda, David I Mostofsky
文献索引:Nutr. Neurosci. 7(2) , 85-90, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Iron deficiency (ID) is among the most common nutritional diseases, causing deleterious effects that include decreases in cognitive function and weight loss. The ID also induces a reduction in the number and affinity of dopaminergic D2 receptors. The new finding that ID induces an increase in the pancreas cells, leads to the hypothesis that cholecystokinin-8 (CCK-8) is involved in the ID effects. The level of CCK-8 was higher among ID rats, compared with normal rats. The ID rats in our study were anorectic and performed poorly in learning tests (Morris water maze and passive avoidance learning). Essential fatty acids (EFA) mediate dopamine activity and have been found to rehabilitate learning deficits. Treatment with a fatty acid compound blocked both the learning deficits and the anorexia, while a CCK-8 antagonist was successful only against the anorectic effects.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
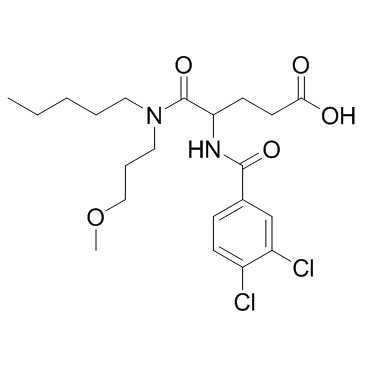 |
氯谷胺
CAS:107097-80-3 |
C21H30Cl2N2O5 |
|
Involvement of capsaicin-sensitive afferent nerves and chole...
2004-07-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 310(1) , 116-25, (2004)] |
|
Effect of cholecystokinin-A receptor blockade on postprandia...
2002-10-01 [Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 14(5) , 519-25, (2002)] |
|
Stimulatory effect of N-methyltyramine, a congener of beer, ...
2010-02-01 [Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 34 Suppl 1 , S14-7, (2010)] |
|
Inhibitory effect of loxiglumide (CR 1505), a cholecystokini...
2002-03-01 [World J. Surg. 26(3) , 359-65, (2002)] |
|
Effects of the cholecystokinin A receptor antagonist loxiglu...
2006-03-01 [Pancreas 32(2) , 190-6, (2006)] |