| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
左乙拉西坦
CAS:102767-28-2 |
|
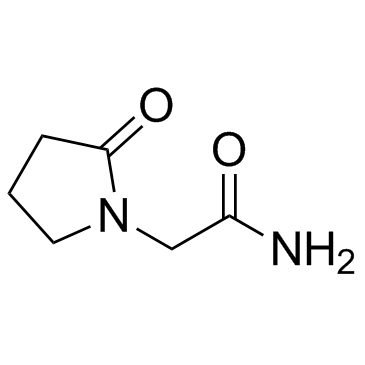 |
吡拉西坦
CAS:7491-74-9 |
|
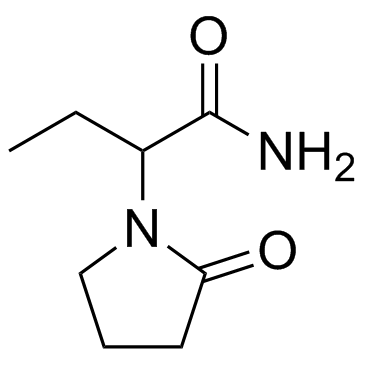 |
乙拉西坦
CAS:33996-58-6 |
|
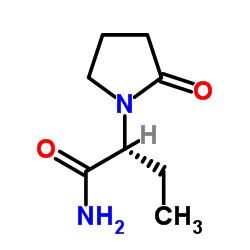 |
(R)-左乙拉西坦
CAS:103765-01-1 |