| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
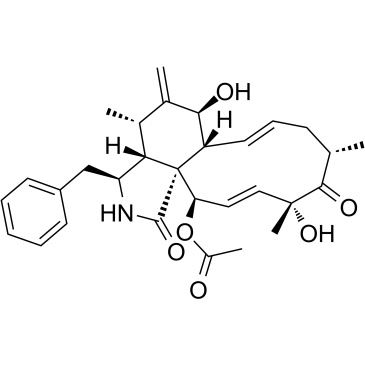 |
细胞松弛素D
CAS:22144-77-0 |
|
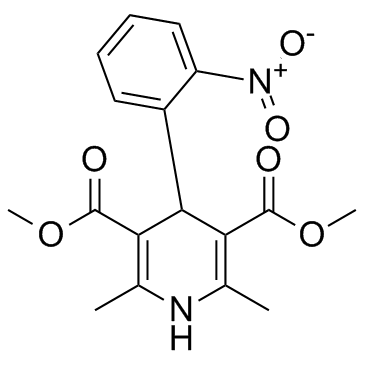 |
硝苯地平
CAS:21829-25-4 |
|
![N-[4-[[1-[2-(6-甲基-2-吡啶基)乙基]-4-哌啶基]羰基]苯基]甲磺酰胺二盐酸盐 结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/420/113559-13-0.png) |
N-[4-[[1-[2-(6-甲基-2-吡啶基)乙基]-4-哌啶基]羰基]苯基]甲磺酰胺二盐酸盐
CAS:113559-13-0 |