| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
丁炔二酸二甲酯
CAS:762-42-5 |
|
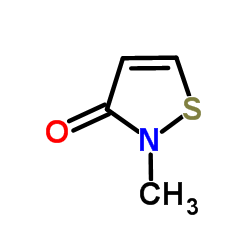 |
甲基异噻唑啉酮
CAS:2682-20-4 |
|
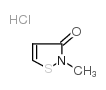 |
2-甲基-4-异噻唑啉-3-酮盐酸盐
CAS:26172-54-3 |