Comparison of pulsed and continuous addition of H2 gas via membranes for stimulating PCE biodegradation in soil columns.
Xin Ma, Paige J Novak, Michael J Semmens, Lee W Clapp, Raymond M Hozalski
文献索引:Water Res. 40(6) , 1155-66, (2006)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Column experiments were performed to investigate a technology for remediating aquifers contaminated with chlorinated solvents. The technology involves installation of hollow-fiber membranes in the subsurface to supply hydrogen gas (H2) to groundwater to support biological reductive dechlorination in situ. Three laboratory-scale columns [control (N2 only), continuous H2, and pulsed H2] were packed with aquifer material from a trichloroethene (TCE)-contaminated wetland in Minnesota and supplied with perchloroethene (PCE)-contaminated synthetic groundwater. The main goals of the research were: (1) evaluate the long-term performance of the H2 supply system and (2) compare the effects of pulsed (4 h on, 20 h off) versus continuous H2 supply (lumen partial pressure approximately 1.2 atm) on PCE dechlorination and production of by-products (i.e. methane and acetate). The silicone-coated fiberglass membranes employed in these experiments were robust, delivering H2 steadily over the entire 349-day experiment. Methane production decreased when H2 was added in a pulsed manner. Nevertheless, the percentage of added H2 used to support methanogenesis was similar in both H2-fed columns (92-93%). For much of the experiment, PCE dechlorination (observed end product = dichloroethene) in the continuous and pulsed H2 columns was comparable, and enhanced in comparison to the natural attenuation observed in the control column. Dechlorination began to decline in the pulsed H2 column after 210 days, however, while dechlorination in the continuous H2 column was sustained. Acetate was detected only in the continuous H2 column, at concentrations of up to 36 microM. The results of this research suggest that in situ stimulation of PCE dechlorination by direct H2 addition requires the continuous application of H2 at high partial pressures, favoring the production of bioavailable organic matter such as acetate to provide a carbon source, electron donor, or both for dechlorinators. Unfortunately, this strategy has proven to be inefficient, with the bulk of the added H2 used to support methanogenesis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
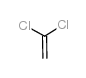 |
1,1-二氯乙烯
CAS:75-35-4 |
C2H2Cl2 |
|
A membrane introduction mass spectrometer utilizing ion-mole...
2015-12-15 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29 , 2187-94, (2015)] |
|
The impact of chlorinated solvent co-contaminants on the bio...
2013-03-01 [Chemosphere 91(1) , 88-92, (2013)] |
|
Acute, subacute, and subchronic oral toxicity studies of 1,1...
2001-11-01 [Toxicol. Sci. 64(1) , 135-45, (2001)] |
|
Bioactivation of 1,1-dichloroethylene to its epoxide by CYP2...
2004-09-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 32(9) , 1032-9, (2004)] |
|
Inhaled chemicals may enhance allergic airway inflammation i...
2006-09-21 [Toxicology 226(2-3) , 161-71, (2006)] |