| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
呋噻米
CAS:54-31-9 |
|
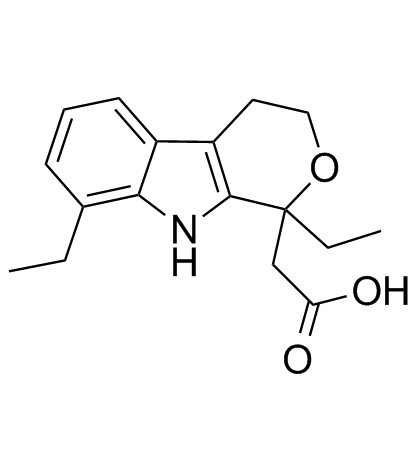 |
依托度酸
CAS:41340-25-4 |
|
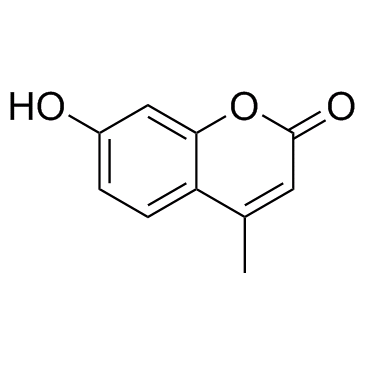 |
4-甲基伞形酮
CAS:90-33-5 |
|
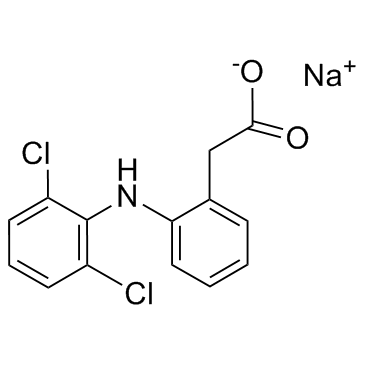 |
双氯芬酸钠
CAS:15307-79-6 |
|
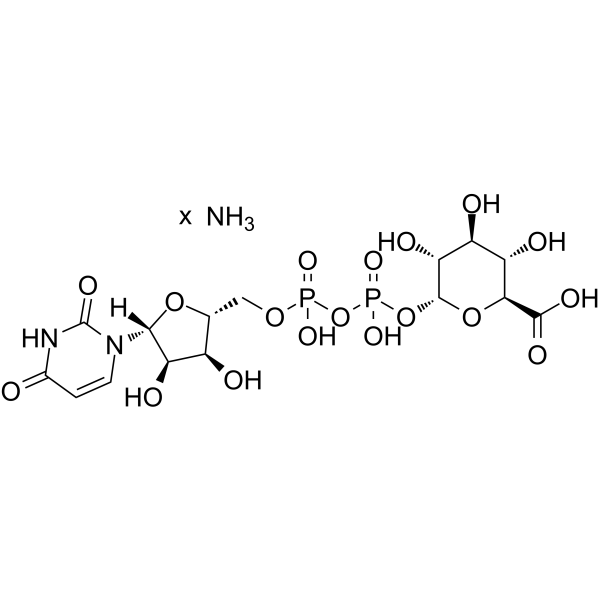 |
尿苷-5′-二磷酸葡糖醛酸 铵盐
CAS:43195-60-4 |
|
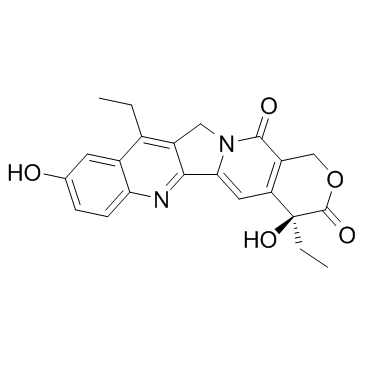 |
7-乙基-10羟基喜树碱
CAS:86639-52-3 |
|
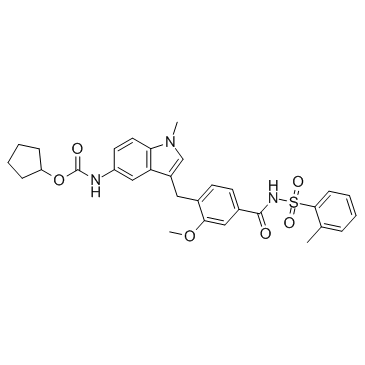 |
扎鲁司特
CAS:107753-78-6 |