Synthesis of 6-aryloxy- and 6-arylalkoxy-2-chloropurines and their interactions with purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Escherichia coli.
A Bzowska, L Magnowska, Z Kazimierczuk
文献索引:Z. Naturforsch., C, J. Biosci. 54(12) , 1055-67, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The phase transfer method was applied to perform the nucleophilic substitution of 2,6-dichloropurines by modified arylalkyl alcohol or phenols. Since under these conditions only the 6-halogen is exchanged, this method gives 2-chloro-6-aryloxy- and 2-chloro-6-arylalkoxy-purines. 2-Chloro-6-benzylthiopurine was synthesized by alkylation of 2-chloro-6-thiopurine with benzyl bromide. The stereoisomers of 2-chloro-6-(1-phenyl-1-ethoxy)purine were obtained from R- and S-enantiomers of sec.-phenylethylalcohol and 2,6-dichloropurine. All derivatives were tested for inhibition with purified hexameric E. coli purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP). For analogues showing IC50 < 10 microM, the type of inhibition and inhibition constants were determined. In all cases the experimental data were best described by the mixed-type inhibition model and the uncompetitive inhibition constant, Kiu, was found to be several-fold lower than the competitive inhibition constant, Kic. This effect seems to be due to the 6-aryloxy- or 6-arylalkoxy substituent, because a natural PNP substrate adenine, as well as 2-chloroadenine, show mixed type inhibition with almost the same inhibition constants Kiu and Kic. The most potent inhibition was observed for 6-benzylthio-2-chloro-, 6-benzyloxy-2-chloro-, 2-chloro-6-(2-phenyl-1-ethoxy), 2-chloro-6-(3-phenyl-1-propoxy)- and 2-chloro-6-ethoxypurines (Kiu = 0.4, 0.6, 1.4, 1.4 and 2.2 microM, respectively). The R-stereoisomer of 2-chloro-6-(1-pheny-1-ethoxy)purine has Kiu = 2.0 microM, whereas inhibition of its S counterpart is rather weak (IC50 > 12 microM). More rigid (e.g. phenoxy-), non-planar (cyclohexyloxy-), or more bulky (2,4,6-trimethylphenoxy-) substituents at position 6 of the purine base gave less potent inhibitors (IC50 = 26, 56 and > 100 microM, respectively). The derivatives are selective inhibitors of hexameric "high-molecular mass" PNPs because no inhibitory activity vs. trimeric Cellulomonas sp. PNP was detected. By establishing the ligand-dependent stabilization pattern of the E. coli PNP it was shown that the new derivatives, similarly as the natural purine bases, are able to form a dead-end ternary complex with the enzyme and orthophosphate. It was also shown that the derivatives are substrates in the reverse synthetic direction catalyzed by E. coli PNP.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
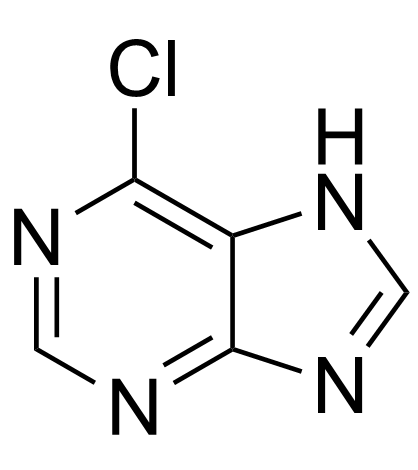 |
6-氯嘌呤
CAS:87-42-3 |
C5H3ClN4 |
|
Synthesis of modified homo-N-nucleosides from the reactions ...
2009-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 6433-6, (2009)] |
|
The synthesis of novel fluorescent purine analogues modified...
2010-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20(10) , 3098-102, (2010)] |
|
Evidence for Watson-Crick and not Hoogsteen or wobble base p...
2005-03-29 [Biochemistry 44(12) , 4850-60, (2005)] |
|
Asymmetric synthesis of novel thioiso dideoxynucleosides wit...
2004-04-30 [J. Org. Chem. 69(9) , 3208-11, (2004)] |
|
Synthesis and biological evaluation of nucleoside analogues ...
2007-05-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 , 2470-3, (2007)] |