| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
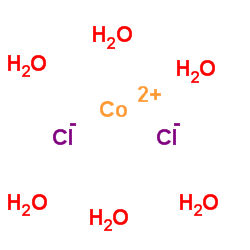 |
氯化钴,六水
CAS:7791-13-1 |
|
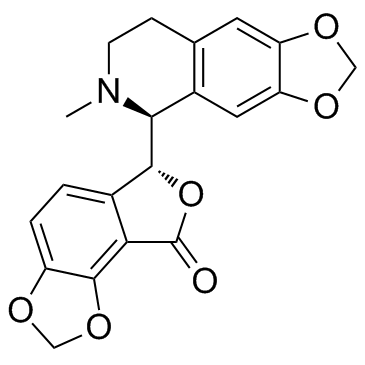 |
(+)-荷包牡丹碱; 右旋荷包牡丹碱; 毕枯枯林; 山乌龟碱
CAS:485-49-4 |
|
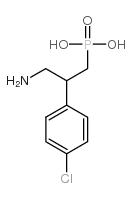 |
3-氨基-2-(4-氯苯基)丙基膦酸
CAS:114012-12-3 |