| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
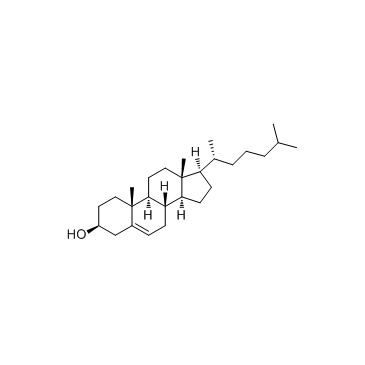 |
胆固醇
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
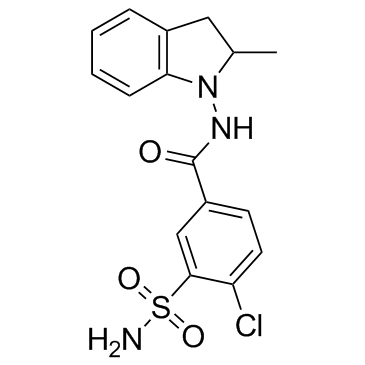 |
吲达帕胺
CAS:26807-65-8 |
|
 |
格列齐特
CAS:21187-98-4 |
|
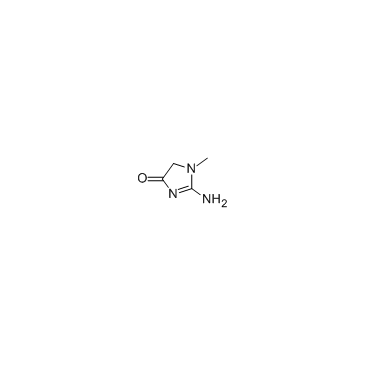 |
肌酐
CAS:60-27-5 |
|
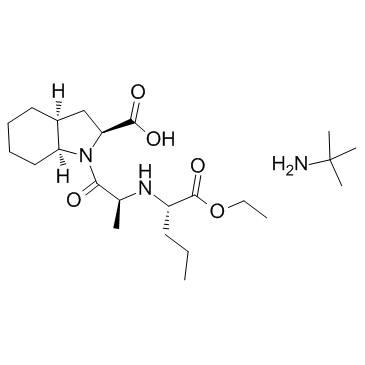 |
培哚普利
CAS:107133-36-8 |