| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
环己烷
CAS:110-82-7 |
|
 |
丁二烯
CAS:106-99-0 |
|
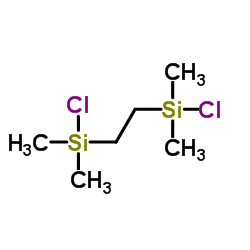 |
1,2-双(氯二甲基硅基)乙烷
CAS:13528-93-3 |
|
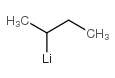 |
仲丁基锂
CAS:598-30-1 |