| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
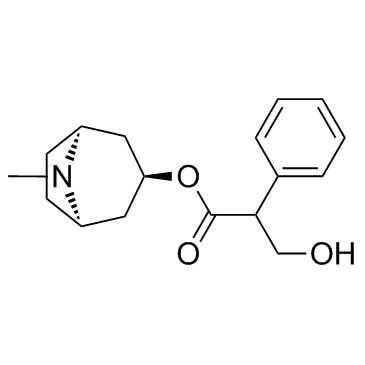 |
阿托品; 颠茄碱
CAS:51-55-8 |
|
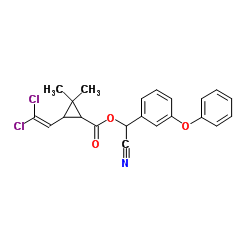 |
氯氰菊酯
CAS:52315-07-8 |
|
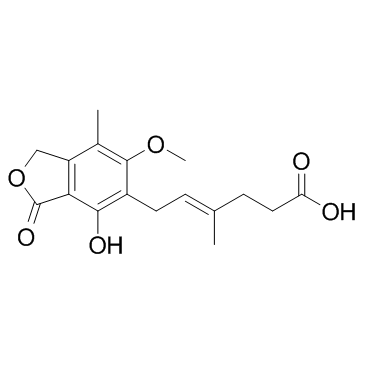 |
霉酚酸
CAS:24280-93-1 |
|
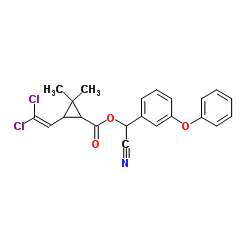 |
右旋反式苯醚菊酯
CAS:67375-30-8 |
|
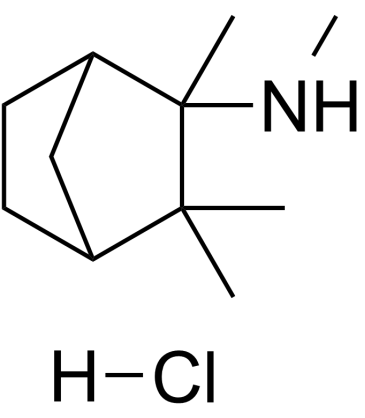 |
盐酸美加明
CAS:826-39-1 |
|
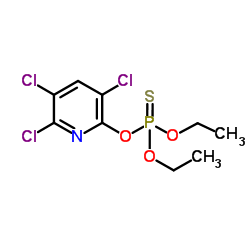 |
毒死蜱
CAS:2921-88-2 |
|
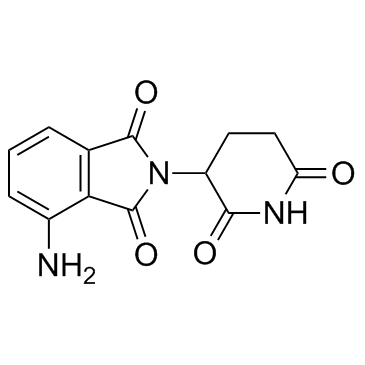 |
泊马度胺
CAS:19171-19-8 |
|
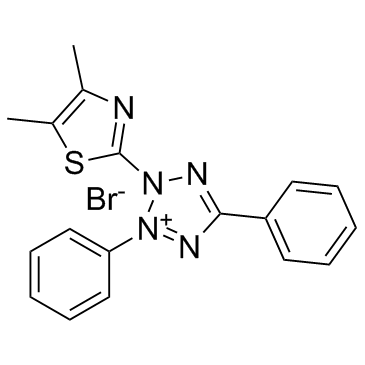 |
噻唑兰
CAS:298-93-1 |