Hydrothermal synthesis of a doped Mn-Cd-S solid solution as a visible-light-driven photocatalyst for H2 evolution.
Keita Ikeue, Satoshi Shiiba, Masato Machida
文献索引:ChemSusChem 4(2) , 269-73, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The effect of metal doping (i.e., with Cr, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag and Sn) on the crystal structure of hydrothermally synthesized Mn(1-x)Cd(x) S (where x≈0.1) is studied with the aim of enhancing photocatalytic activity. In contrast to the low-crystalline, undoped solid solution Mn(1-x)Cd(x)S, Ni doping yields a well-crystallized wurtzite-type Mn-Cd-S solid solution, which precipitates as planar hexagonal facets of several hundred nanometers in size, together with much larger grains of α-MnS (>10 μm). By removing inactive α-MnS through sedimentation, a single phase with composition of Ni(0.01)Mn(0.56)Cd(0.43)S is obtained successfully. The Ni doping achieved a threefold higher photocatalytic activity for H(2) evolution from a 0.1 M Na(2)S/0.5 M Na(2)SO(3) solution under visible-light irradiation (λ≥420 nm). The apparent quantum yield of 1 wt % Pt-loaded Ni(0.01)Mn(0.56)Cd(0.43)S measured at λ=420 nm reached 25 %. The enhanced photocatalytic activity is most likely the result of a decreased concentration of defects, responsible for electron-hole recombination, in the active solid-solution phase and a slightly higher bandgap energy (2.4 eV).Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
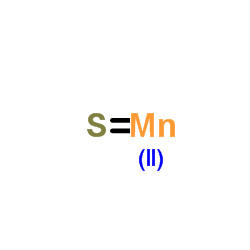 |
硫化锰
CAS:18820-29-6 |
MnS |
|
Unusual formation of single-crystal manganese sulfide microb...
2012-07-16 [Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 51(29) , 7267-70, (2012)] |
|
Rapid and effective labeling of brain tissue using TAT-conju...
2005-07-07 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) (25) , 3144-6, (2005)] |
|
Carcinogenic sulfide salts of nickel and cadmium induce H2O2...
1990-12-01 [Cancer Res. 50(23) , 7564-70, (1990)] |
|
Use of a paramagnetic substance, colloidal manganese sulfide...
1984-05-01 [J. Nucl. Med. 25(5) , 604-7, (1984)] |
|
The big red shift of photoluminescence of Mn dopants in stra...
2010-05-19 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(19) , 6618-9, (2010)] |