The big red shift of photoluminescence of Mn dopants in strained CdS: a case study of Mn-doped MnS-CdS heteronanostructures.
Taisen Zuo, Zhipeng Sun, Yuliang Zhao, Xiaoming Jiang, Xueyun Gao
文献索引:J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(19) , 6618-9, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The red photoluminescence of Mn dopants in MnS-CdS heteronanostructures has been observed for the first time. The red photoluminescence at 650 nm derives from emission due to the (4)T(1) --> (6)A(1) transition of Mn(2+) dopants in a CdS matrix exposed to gigapascal-level lattice stress. HRTEM, FFT, XRD, and optical studies revealed that the lattice of Mn-doped CdS is compressed to match that of MnS when CdS crystallizes at the MnS surface to form MnS-CdS heteronanostructures. The photoluminescence decay times of such Mn dopants are on the order of nanoseconds because of the spin-flip interactions between Mn dopants and free carriers in the CdS matrix.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
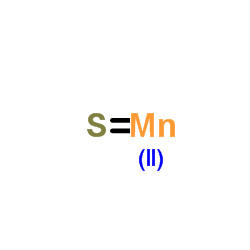 |
硫化锰
CAS:18820-29-6 |
MnS |
|
Unusual formation of single-crystal manganese sulfide microb...
2012-07-16 [Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 51(29) , 7267-70, (2012)] |
|
Rapid and effective labeling of brain tissue using TAT-conju...
2005-07-07 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) (25) , 3144-6, (2005)] |
|
Carcinogenic sulfide salts of nickel and cadmium induce H2O2...
1990-12-01 [Cancer Res. 50(23) , 7564-70, (1990)] |
|
Use of a paramagnetic substance, colloidal manganese sulfide...
1984-05-01 [J. Nucl. Med. 25(5) , 604-7, (1984)] |
|
Mineral-assisted pathways in prebiotic synthesis: photoelect...
2004-09-15 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(36) , 11247-53, (2004)] |