| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
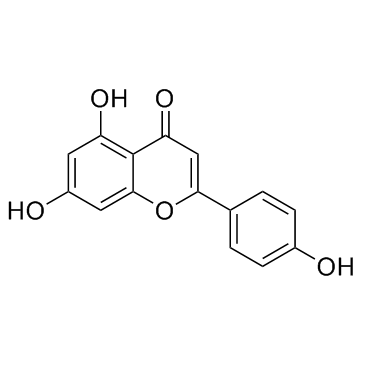 |
芹菜素; 芹黄素; 5,7,4'-三羟基黄酮
CAS:520-36-5 |
|
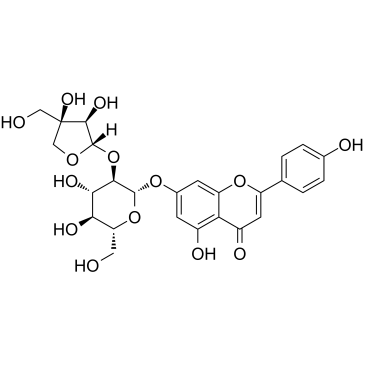 |
芹菜苷
CAS:26544-34-3 |