| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
马来酸美西麦角
CAS:129-49-7 |
|
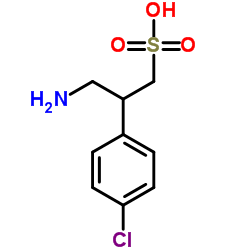 |
β-(氨基甲基)-4 氯代苯乙烷磺酸
CAS:125464-42-8 |