| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
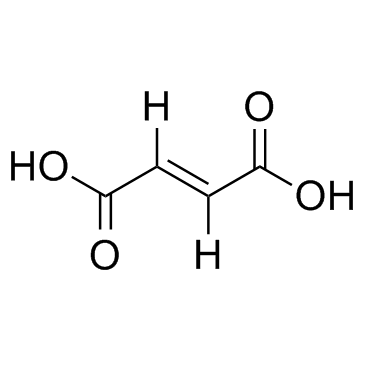 |
富马酸,反丁烯二酸
CAS:110-17-8 |
|
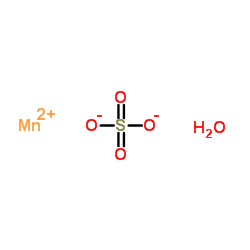 |
一水合硫酸锰
CAS:10034-96-5 |
|
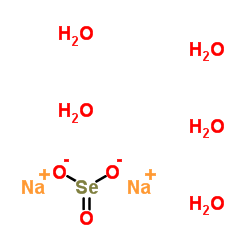 |
亚硒酸钠(五水)
CAS:26970-82-1 |
|
 |
亚硒酸钠
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
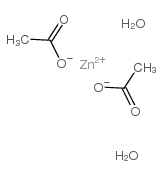 |
乙酸锌,二水
CAS:5970-45-6 |
|
 |
亚硒酸氢钠
CAS:7782-82-3 |