| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
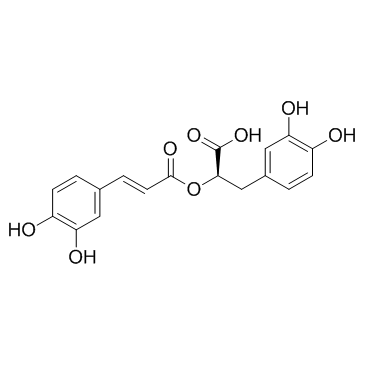 |
迷迭香酸
CAS:20283-92-5 |
|
 |
鼠尾草酚
CAS:5957-80-2 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
迷迭香酸
CAS:20283-92-5 |
|
 |
鼠尾草酚
CAS:5957-80-2 |