| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
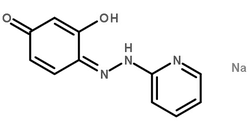 |
大豆油
CAS:8001-22-7 |
|
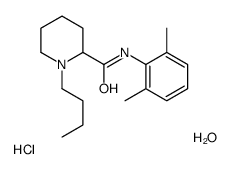 |
盐酸布比卡因
CAS:73360-54-0 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
大豆油
CAS:8001-22-7 |
|
 |
盐酸布比卡因
CAS:73360-54-0 |