| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
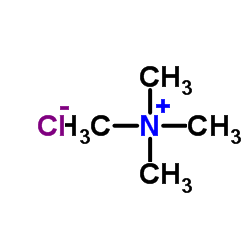 |
四甲基氯化铵
CAS:75-57-0 |
|
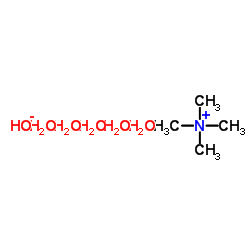 |
四甲基氢氧化铵五水合物
CAS:10424-65-4 |
|
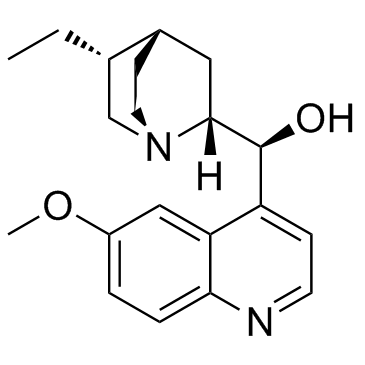 |
二氢奎尼丁
CAS:1435-55-8 |
|
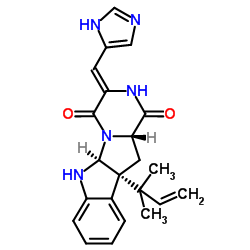 |
Roquefortine C
CAS:58735-64-1 |
|
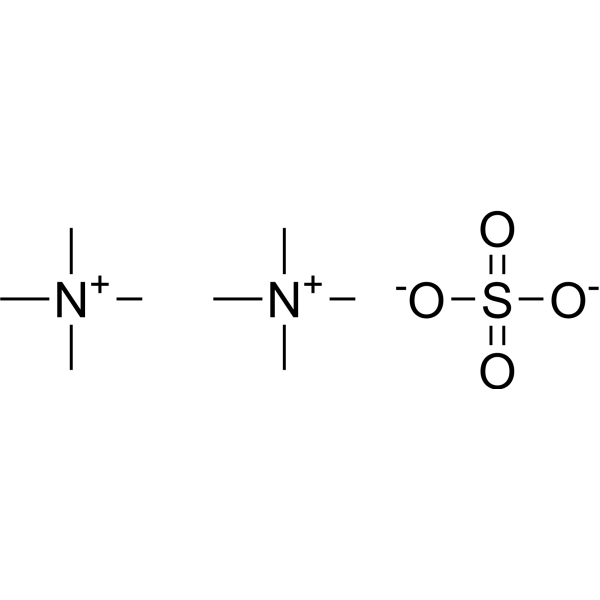 |
四甲基硫酸铵
CAS:14190-16-0 |
|
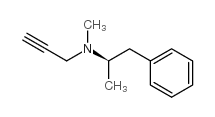 |
司来吉兰 盐酸盐
CAS:14611-51-9 |