| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
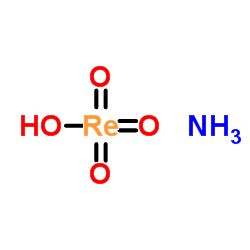 |
高铼酸铵
CAS:13598-65-7 |
|
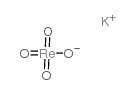 |
过铼酸钾
CAS:10466-65-6 |
|
 |
高铼酸钠
CAS:13472-33-8 |