A direct sulfhydrylation pathway is used for methionine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
M Foglino, F Borne, M Bally, G Ball, J C Patte
文献索引:Microbiology 141 ( Pt 2) , 431-9, (1995)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The relationship between genes and enzymes in the methionine biosynthetic pathway has been studied in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The first step is catalysed by an O-succinylhomoserine synthase, the product of the metA gene mapped at 20 min on the chromosome. The second step is achieved by direct sulfhydrylation, involving the enzyme encoded by a metZ gene that we have identified and sequenced, located at 40 min. Thus Pseudomonas appears to be the only organism so far described that uses O-succinylhomoserine as substrate for a direct sulfhydrylation. As in yeast, the two transsulfuration pathways between cysteine and homocysteine, with cystathionine as an intermediate, probably exist in parallel in this organism.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
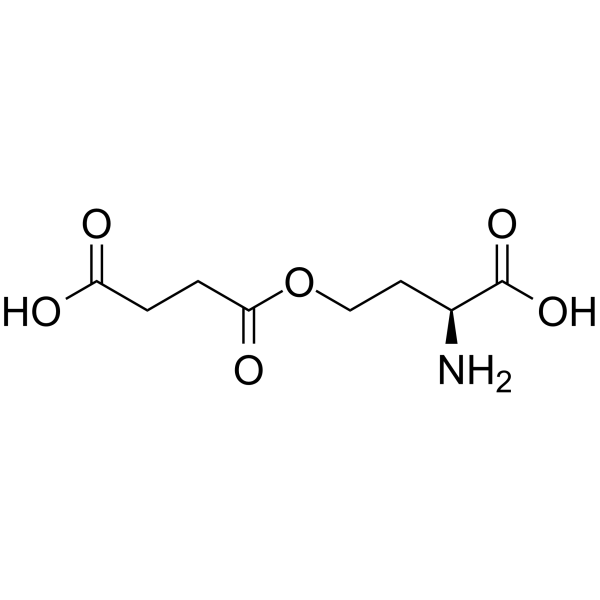 |
O-琥珀酰-L-高丝氨酸
CAS:1492-23-5 |
C8H13NO6 |
|
The enzymology of cystathionine biosynthesis: strategies for...
2005-01-01 [Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 433 , 166-175, (2005)] |
|
Cloning and characterization of two Lactobacillus casei gene...
2008-01-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74 , 99-106, (2008)] |
|
Enzymatic characterization and inhibitor discovery of a new ...
2008-01-01 [J. Biochem. 143 , 59-68, (2008)] |
|
Pathways of assimilative sulfur metabolism in Pseudomonas pu...
1999-09-01 [J. Bacteriol. 181(18) , 5833-7, (1999)] |
|
Cloning and characterization of the CYS3 (CYI1) gene of Sacc...
1992-05-01 [J. Bacteriol. 174(10) , 3339-47, (1992)] |