Effects of aliphatic nitriles in micromass cultures of rat embryo limb bud cells.
Anne-Marie Saillenfait, Jean-Philippe Sabaté, Christiane Gaspard
文献索引:Toxicol. In Vitro 18(3) , 311-8, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The relative effects of a series of eight saturated (acetonitrile, propionitrile and n-butyronitrile) and unsaturated (acrylonitrile, allylnitrile, methacrylonitrile, cis-2-pentenenitrile, and 2-chloroacrylonitrile) aliphatic nitriles were evaluated using an in vitro test for embryotoxicity, the rat limb bud micromass assay. The concentrations that produced 50% inhibition (IC50) of viability and differentiation of the cultured embryonic cells were of the same order of magnitude, whatever tested compound. The IC50 values spread over a wide concentration range from 7-11 microM to 150 mM. Acetonitrile and 2-chloroacrylonitrile were the least and most potent compounds, respectively. The tested chemicals were evaluated using different criteria proposed to identify teratogens in the micromass system, based on either active concentrations or specific inhibition of cell differentiation. A few incorrect classifications were obtained with both nonteratogens and teratogens, when comparing the activity in limb bud cell cultures with the data available on their in vivo teratogenic potential in rats. The concordance between the in vitro and in vivo responses of this set of nitriles was judged insufficient to consider the micromass assay valuable for predicting the in vivo teratogenic outcome of this class of compounds.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
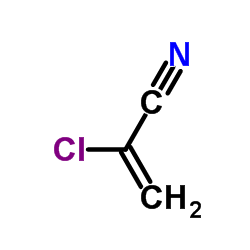 |
2-氯丙烯腈
CAS:920-37-6 |
C3H2ClN |
|
Structure-nephrotoxicity relationships of glutathione pathwa...
1989-05-31 [Toxicology 56(1) , 47-61, (1989)] |
|
[Information from the Soviet Toxicology Center].
1983-02-01 [Gig. Tr. Prof. Zabol. (2) , 52-3, (1983)] |
|
Dual-function cinchona alkaloid catalysis: catalytic asymmet...
2006-03-29 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128(12) , 3928-30, (2006)] |
|
Asymmetric conjugate addition of oxindoles to 2-chloroacrylo...
2010-12-27 [Chemistry 16(48) , 14290-4, (2010)] |
|
Genotoxicity of 2-halosubstituted enals and 2-chloroacryloni...
1994-10-01 [Mutat. Res. 322(4) , 321-8, (1994)] |