Mechanisms of action of pyrazolopyrimidines in Leishmania donovani.
D L Looker, J J Marr, R L Berens
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 261(20) , 9412-5, (1986)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We investigated the antileishmanial actions of the pyrazolopyrimidines allopurinol (4-hydroxypyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine), thiopurinol (4-thiopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine), and aminopurinol (4-aminopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine). These compounds affect several metabolic processes. The first is the inhibition of GMP reductase by the IMP analogues allopurinol ribonucleoside monophosphate and thipurinol ribonucleoside monophosphate which reduces the organism's ability to synthesize ATP from guanine. Second, interconversion of adenine nucleotides to guanine nucleotides, is curtailed by the inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase by these same IMP analogues. Third, the IMP analogues reduce intracellular UTP content. The fourth affect is increased catabolism of RNA and consequent reduction of protein synthesis. This latter effect is due to the adenine nucleotide analogues aminopurinol ribonucleoside mono-, di-, and/or triphosphates, metabolic products of both allopurinol and aminopurinol.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
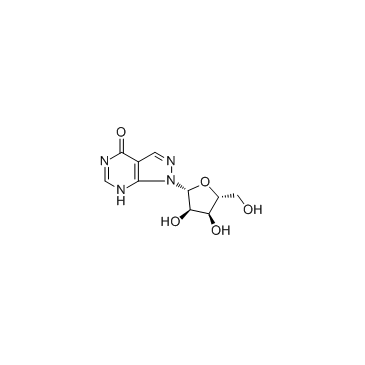 |
别嘌呤醇核糖苷
CAS:16220-07-8 |
C10H12N4O5 |
|
Activity of inosine analogs against Pneumocystis carinii in ...
1986-07-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 30(1) , 181-3, (1986)] |
|
A tissue culture system for the growth of several species of...
1988-03-01 [Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 38(2) , 304-7, (1988)] |
|
On the metabolism of allopurinol. Formation of allopurinol-1...
1983-07-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 32(14) , 2167-74, (1983)] |
|
Efficacy of pyrazolopyrimidine ribonucleosides against Trypa...
1984-10-01 [J. Infect. Dis. 150(4) , 602-8, (1984)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of allopurinol riboside.
1991-05-01 [Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 49(5) , 506-14, (1991)] |