| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
雌三醇
CAS:50-27-1 |
|
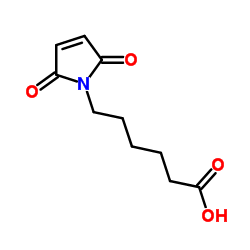 |
6-马来酰亚氨基己酸
CAS:55750-53-3 |
|
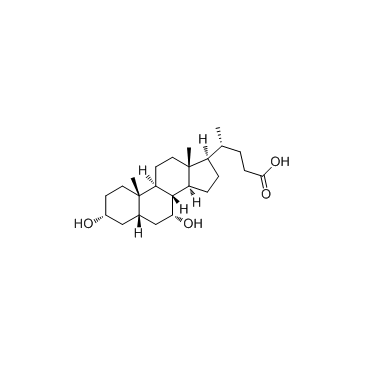 |
鹅去氧胆酸; 鹅脱氧胆酸
CAS:474-25-9 |
|
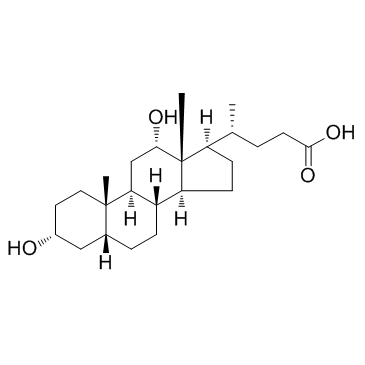 |
去氧胆酸
CAS:83-44-3 |
|
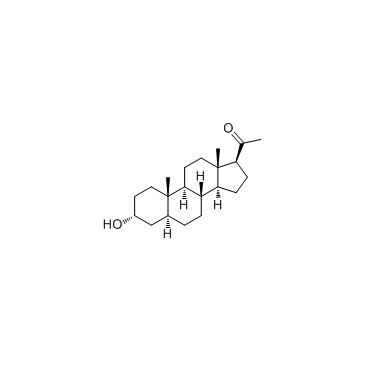 |
5alpha-孕甾-3alpha-醇-20-酮
CAS:516-54-1 |
|
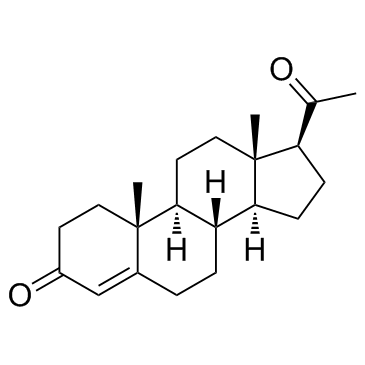 |
孕酮; 黄体素; 黄体酮
CAS:57-83-0 |
|
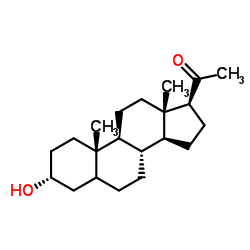 |
孕烷醇酮
CAS:128-20-1 |
|
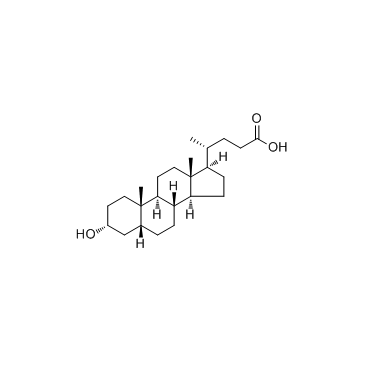 |
石胆酸
CAS:434-13-9 |
|
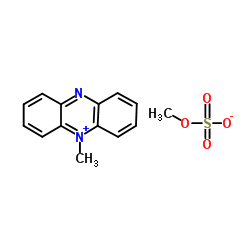 |
5-甲基吩嗪硫酸甲酯
CAS:299-11-6 |
|
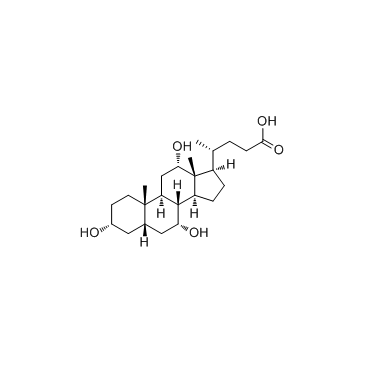 |
胆酸
CAS:81-25-4 |