| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
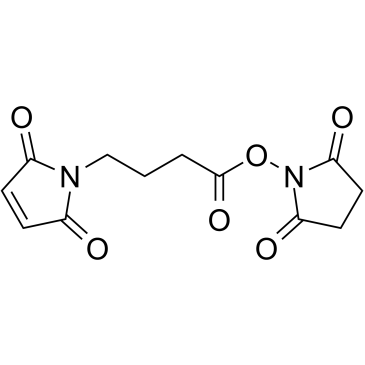 |
N-(4-马来酰亚胺丁酰基)琥珀酰亚胺
CAS:80307-12-6 |
|
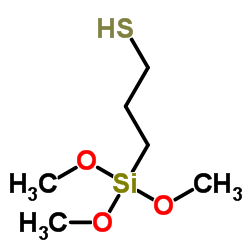 |
巯丙基三甲氧基硅烷
CAS:4420-74-0 |
|
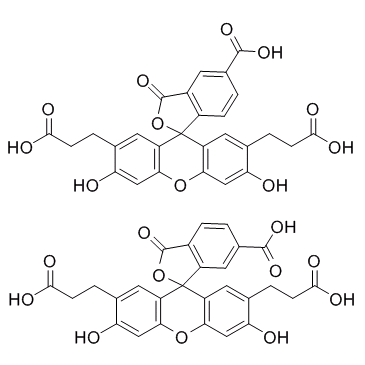 |
2,7-双-(羧乙基)-羧基-荧光素
CAS:85138-49-4 |