Comparison of antibody functionality using different immobilization methods.
R Danczyk, B Krieder, A North, T Webster, H HogenEsch, A Rundell
文献索引:Biotechnol. Bioeng. 84(2) , 215-23, (2003)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
This study investigates the influence of antibody immobilization methods on antigen capture. Adsorption and two surface chemistries, an aminosilane chemistry and a common heterobifunctional crosslinker (N-gamma-maleimidobutyryloxy-succinimide ester, GMBS), were compared and evaluated for their ability to immobilize antibodies and capture antigen. The role of protein A as an orienting protein scaffold component in each of these techniques was also evaluated. Through experimentation it was determined that the GMBS technique immobilized the highest amount of antibody and minimized nonspecific binding. For all techniques, the most functional antibodies were found to be those immobilized with protein A. Interestingly, the aminosilane technique demonstrated the highest antigen capture with antibody alone but also exhibited the highest level of nonspecific binding.Copyright 2003 Wiley Periodicals.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
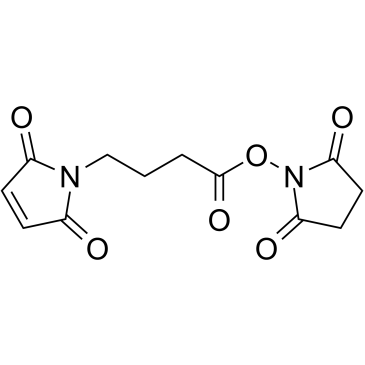 |
N-(4-马来酰亚胺丁酰基)琥珀酰亚胺
CAS:80307-12-6 |
C12H12N2O6 |
|
Highly efficient capture and harvest of circulating tumor ce...
2015-04-01 [Biomed. Microdevices 17(2) , 39, (2015)] |
|
A chitosan coated monolith for nucleic acid capture in a the...
2014-07-01 [Biomicrofluidics 8(4) , 044109, (2014)] |
|
Expansion of CTCs from early stage lung cancer patients usin...
2014-12-15 [Oncotarget 5(23) , 12383-97, (2015)] |
|
Investigation on the reaction conditions of Staphylococcus a...
2014-08-01 [Anticancer Res. 34(8) , 4521-7, (2014)] |
|
Developing a programmed restriction endonuclease for highly ...
2005-01-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 33(22) , 7039-47, (2005)] |