| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
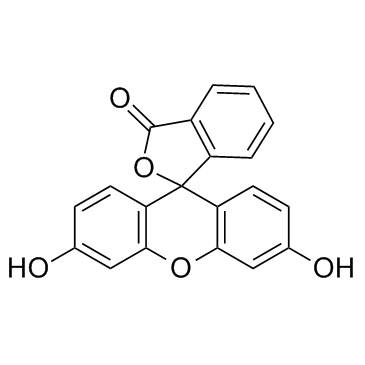 |
荧光素
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
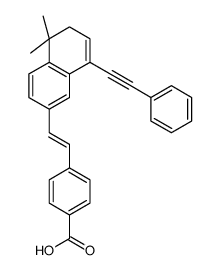 |
BMS493
CAS:215030-90-3 |
|
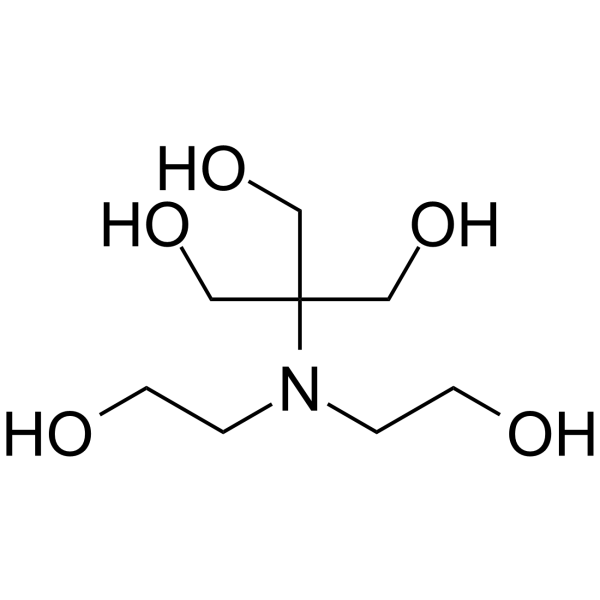 |
二(2-羟乙基)亚氨基三(羟甲基)甲烷
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
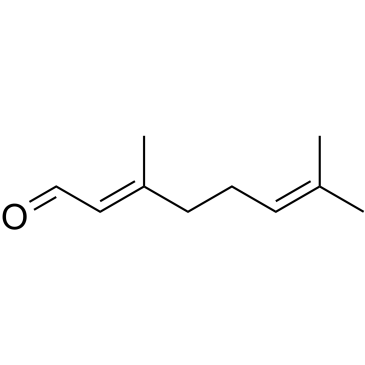 |
柠檬醛
CAS:5392-40-5 |
|
 |
维生素A酸; 视黄酸
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
 |
环丙沙星
CAS:85721-33-1 |