| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
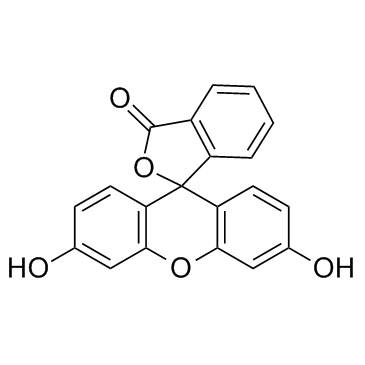 |
荧光素
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
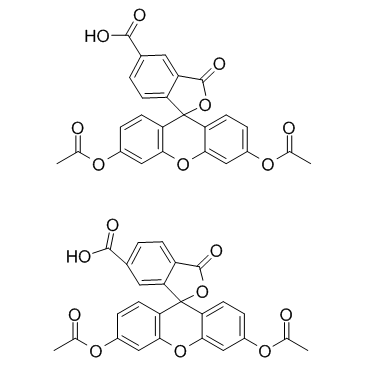 |
5(6)-羧基荧光素二乙酸酯
CAS:124387-19-5 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
荧光素
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
 |
5(6)-羧基荧光素二乙酸酯
CAS:124387-19-5 |