| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
十二烷基硫酸钠
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
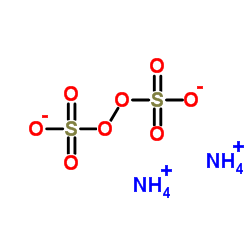 |
过硫酸铵
CAS:7727-54-0 |
|
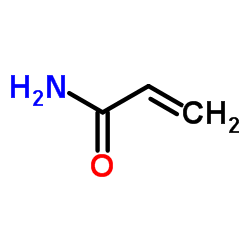 |
丙烯酰胺
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
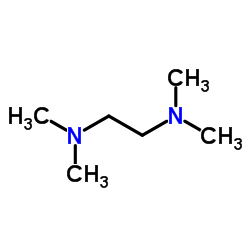 |
四甲基乙二胺(TEMED)
CAS:110-18-9 |
|
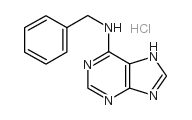 |
6-苄氨基嘌呤 盐酸盐
CAS:162714-86-5 |
|
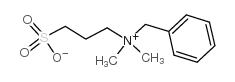 |
3-(苄基二甲基铵基)丙烷基磺酸
CAS:81239-45-4 |
|
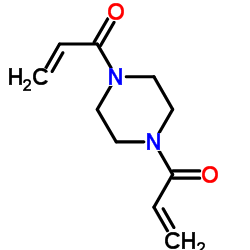 |
1,4-二丙烯酰基哌嗪
CAS:6342-17-2 |
|
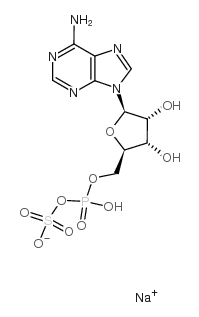 |
腺苷5-磷酰硫酸二钠盐
CAS:102029-95-8 |