| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
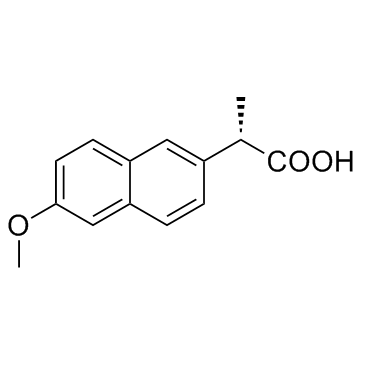 |
萘普生
CAS:22204-53-1 |
|
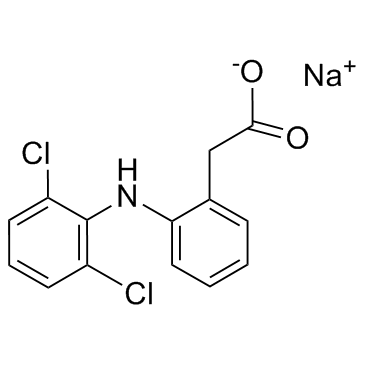 |
双氯芬酸钠
CAS:15307-79-6 |
|
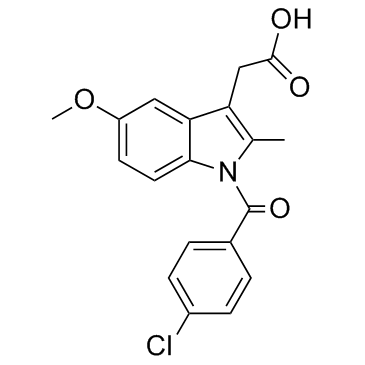 |
吲哚美辛
CAS:53-86-1 |
|
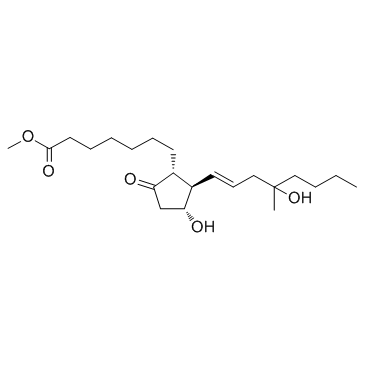 |
米索前列醇
CAS:59122-46-2 |