| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘氨酸
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
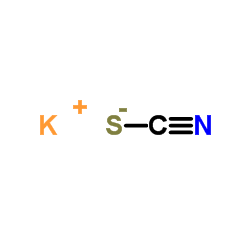 |
硫氰酸钾
CAS:333-20-0 |
|
 |
4',6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚二盐酸盐
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
 |
DL-2-氨基丙酸
CAS:302-72-7 |