| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
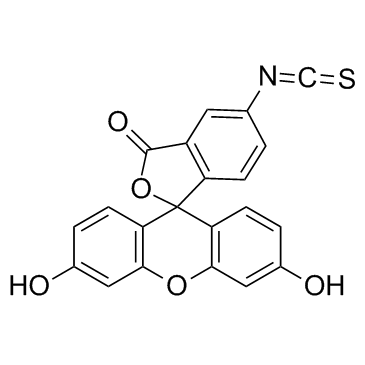 |
异硫氰酸荧光素酯
CAS:3326-32-7 |
|
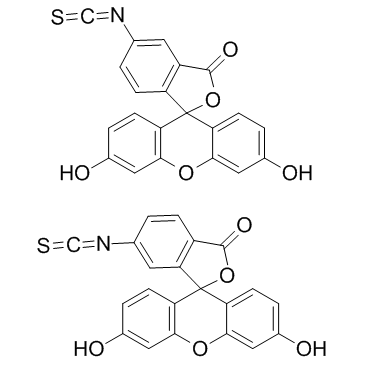 |
异硫氰酸荧光素
CAS:27072-45-3 |
|
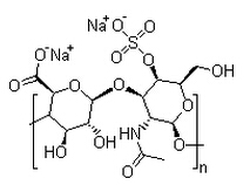 |
硫酸软骨素A钠盐
CAS:39455-18-0 |
|
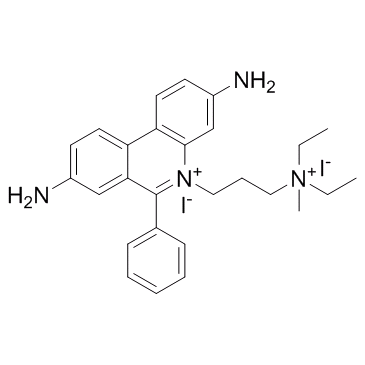 |
碘化丙啶
CAS:25535-16-4 |