| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
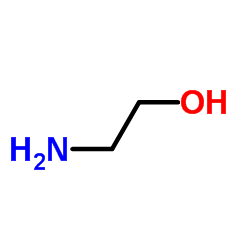 |
2-氨基乙醇
CAS:141-43-5 |
|
 |
钙
CAS:7440-70-2 |
|
 |
抗坏血酸
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
无水氯化钙
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
4-羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
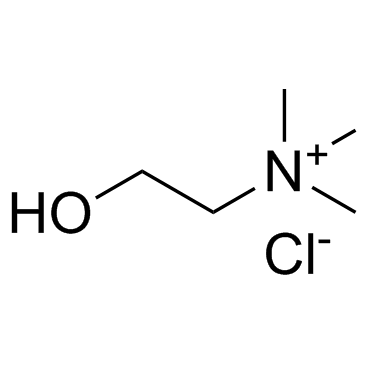 |
氯化胆碱
CAS:67-48-1 |
|
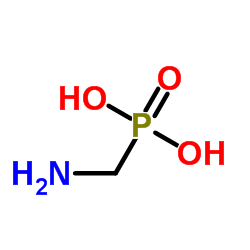 |
氨甲基膦酸
CAS:1066-51-9 |
|
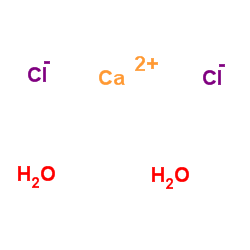 |
二水氯化钙
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
 |
桃叶珊瑚苷; 杜仲苷
CAS:479-98-1 |
|
 |
盐酸美金刚
CAS:41100-52-1 |